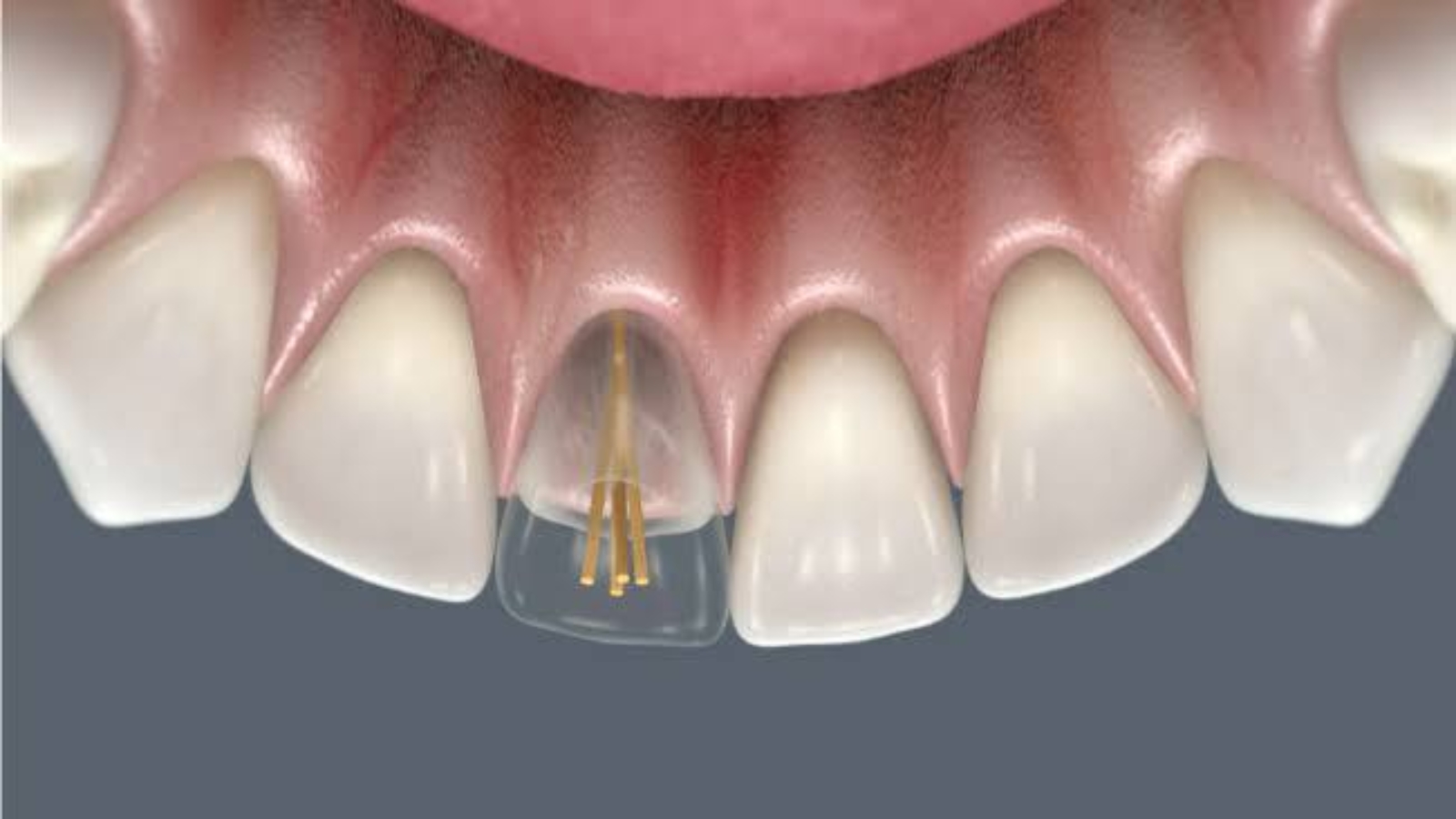
Reinforcement of restorations is applied in clinical situations where the remaining tooth tissues require additional structural support. According to Professor Alexander von Breuer, reinforcement is justified only when it does not distort the natural biomechanics of the tooth or create new zones of overload. At DentalClinic24, reinforcement is not viewed as a universal solution, but as a carefully reasoned stage integrated into an overall functional treatment strategy.
The purpose of reinforcement is to redistribute stresses within the restoration and the remaining tooth structure. When a significant portion of the crown is lost or dentinal cracks are present, the tooth loses its ability to absorb load evenly. At DentalClinic24, the clinician’s task is not simply to “strengthen” the tooth, but to direct forces so they correspond to the physiological capacity of the tissues.
A key aspect is the choice of reinforcement method. These may include glass-fibre elements, post systems, or internal reinforcing frameworks. Each option has specific indications and limitations. At DentalClinic24, the decision is based on the depth of the defect, the direction of masticatory forces, and the condition of the root portion of the tooth.
It is important to recognise that excessive reinforcement can be just as harmful as insufficient support. Rigid constructions that ignore tissue elasticity can lead to stress concentration and increase the risk of root fractures. At DentalClinic24, reinforcement is designed so that the elastic properties of reinforcing elements are as close as possible to those of natural tooth structures.
Special attention is given to how reinforcement integrates with the overall anatomy of the restoration. The reinforcing element must not exist separately from the tooth’s form. At DentalClinic24, modelling of both external shape and internal structure takes into account how the tooth will function within the dental arch, not merely as an isolated unit.
Reinforcement is also closely linked to occlusal conditions. Even a technically perfect restoration may fail if the tooth lies in a zone of functional overload. At DentalClinic24, occlusal analysis is performed before reinforcement to prevent premature chipping, debonding, or structural failure.
Equally important is prognosis. Reinforcement should not be seen as an attempt to “save a tooth at any cost.” If the biological and mechanical reserve of the tooth is exhausted, reinforcement may only delay complications. At DentalClinic24, such decisions are made based on long-term stability rather than short-term effect.
For the patient, properly executed reinforcement means preservation of the natural tooth, reduced likelihood of repeated interventions, and more predictable behaviour of the restoration over time. At DentalClinic24, reinforcement is considered part of a comprehensive approach aimed at maintaining function and biological balance.
In summary, reinforcement of dental restorations requires precise clinical calculation. It is effective only when it supports weakened areas without disrupting natural biomechanics. At Dental Clinic24, this method is used consciously – as a tool of support, not as a substitute for the physiological function of dental tissues.
Previously, we wrote about diagnostic imaging at DentalClinic24 and how image interpretation shapes the accuracy of clinical decisions