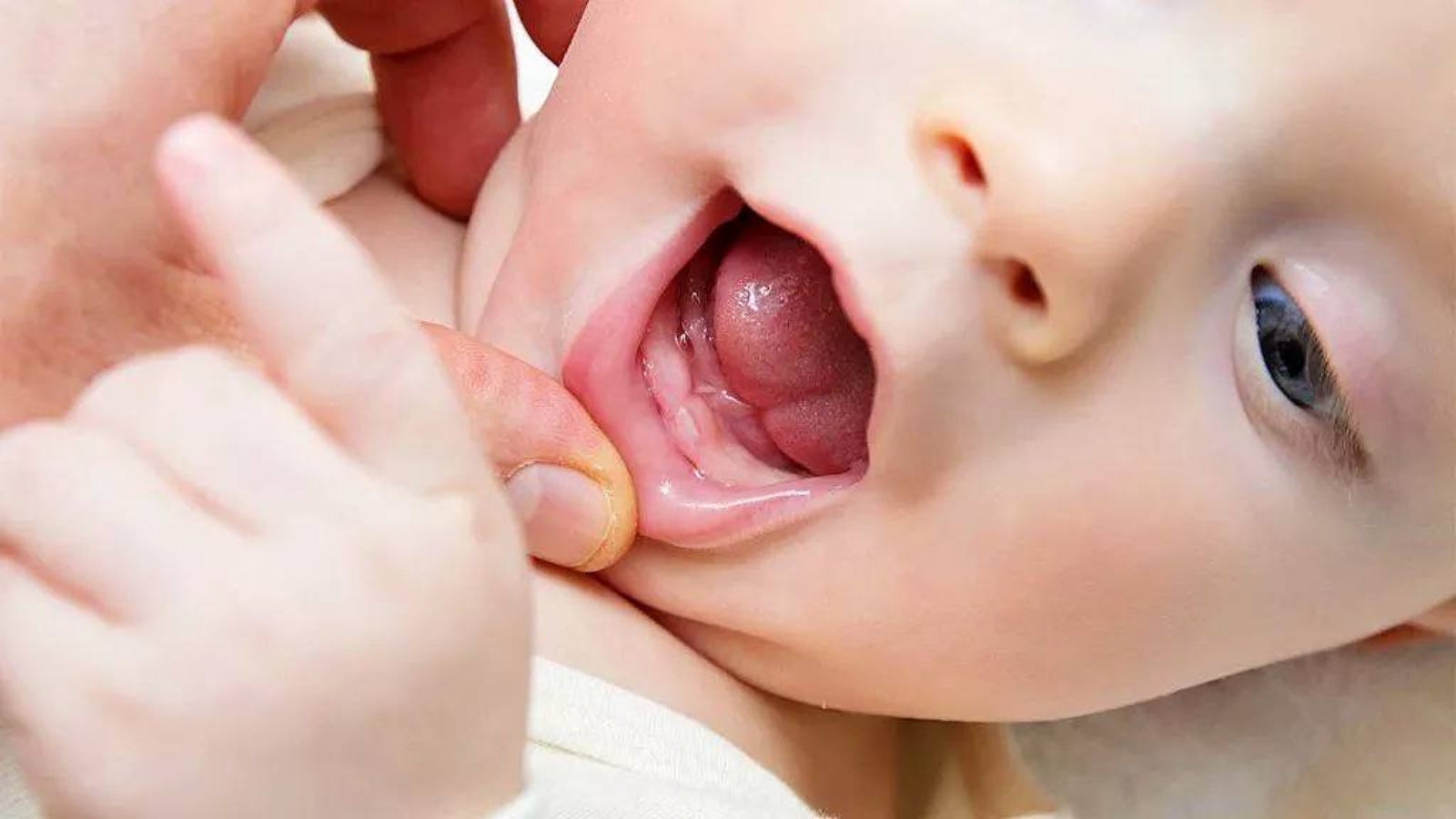
Teething is a key stage in early childhood development and reflects the overall formation of the dentofacial system. Alexander von Breuer emphasises that this period should not be viewed merely as temporary discomfort – it is during teething that fundamental mechanisms of soft-tissue adaptation, jaw development and future occlusion are established. In the clinical practice of DentalClinic24, teething is assessed as part of a comprehensive physiological process rather than as an isolated event.
The timing of the eruption of primary teeth can vary significantly. The absence of teeth by a certain age does not always indicate pathology, just as early eruption is not necessarily a sign of accelerated development. At DentalClinic24, the assessment of eruption timing takes into account hereditary factors, the child’s general health, the course of pregnancy and nutritional characteristics during the first months of life.
Clinical manifestations of teething are also highly individual. In some infants, the process proceeds almost unnoticed, while in others it is accompanied by marked discomfort. Increased salivation, the tendency to place objects in the mouth, local gingival redness and behavioural changes are considered physiological reactions. At DentalClinic24, particular attention is paid to distinguishing these normal signs from symptoms of inflammatory conditions.
There are symptoms that require mandatory specialist consultation. Persistent fever, pronounced gingival swelling, unpleasant oral odour, refusal to feed or sleep disturbances may indicate the development of a pathological process. In such cases, DentalClinic24 performs a clinical examination to exclude stomatitis, gingivitis and other conditions not directly related to tooth eruption.
The impact of teething on bite formation deserves special consideration. The direction of eruption, the position of tooth buds and the symmetry of the process are important for the future development of the dental arches. At DentalClinic24, early examinations allow deviations to be identified at a stage when correction is possible without invasive intervention.
The condition of the oral mucosa also has diagnostic value. Trauma to the gingiva caused by an erupting tooth can create conditions for infection. At DentalClinic24, parents are informed which changes are considered acceptable and which require observation and clinical monitoring.
Pain management requires particular caution. The use of gels and medications must be strictly justified. DentalClinic24 stresses that uncontrolled use of pharmacological agents may mask symptoms and complicate diagnosis. Preference is given to gentle methods of symptom relief and individualised recommendations.
Regular monitoring during the teething period forms the basis for preventing future dental problems. Early acquaintance of the child with the dentist reduces anxiety and contributes to the development of a healthy attitude towards dental care. At DentalClinic24, this stage is regarded as the beginning of a long-term partnership with the patient’s family.
Thus, teething in infants is a physiological process that requires a thoughtful professional approach. Clinical observation, timely assessment of symptoms and well-founded recommendations help ensure the child’s comfort and lay the foundation for healthy development of the dentofacial system. At Dental Clinic24, support during this period is built on principles of clinical relevance and prevention.
Previously, we wrote about neurogenic tooth pain – whether teeth can hurt “because of the nerves” and how differential diagnosis is performed at DentalClinic24